What is Mechanical Ventilation?
Mechanical ventilation is a medical intervention used to assist or replace spontaneous breathing in patients who cannot breathe adequately on their own. It delivers oxygen to the lungs and removes carbon dioxide from the body, often used in cases of respiratory failure, severe lung infections, or during surgery when anesthesia impairs natural breathing.
Mechanical ventilation involves several key components, each serving a crucial function to support or control a patient's breathing.
Ventilator
Ventilator is a machine that takes over the work of breathing when a person is not able to breathe enough on their own. A ventilator can provide different ventilation modes depending on the patient's clinical condition. Ventilation modes can generally be classified into Full Support or Partial Support, depending on the level of assistance provided to the patient.
Breathing circuit

Breathing Circuit can be best described as the lifeline between the patient and the mechanical ventilator consists of various combinations of interfaces, enabling the delivery of medical gas to patients in a consistent and highly regulated manner. GaleMed has extensive OEM experience and can customize various types of breathing circuits according to customer requirements.
Explore our different types of Breathing Circuit
Different Types of breathing Circuit
Breathing circuits can be classified based on several characteristics:
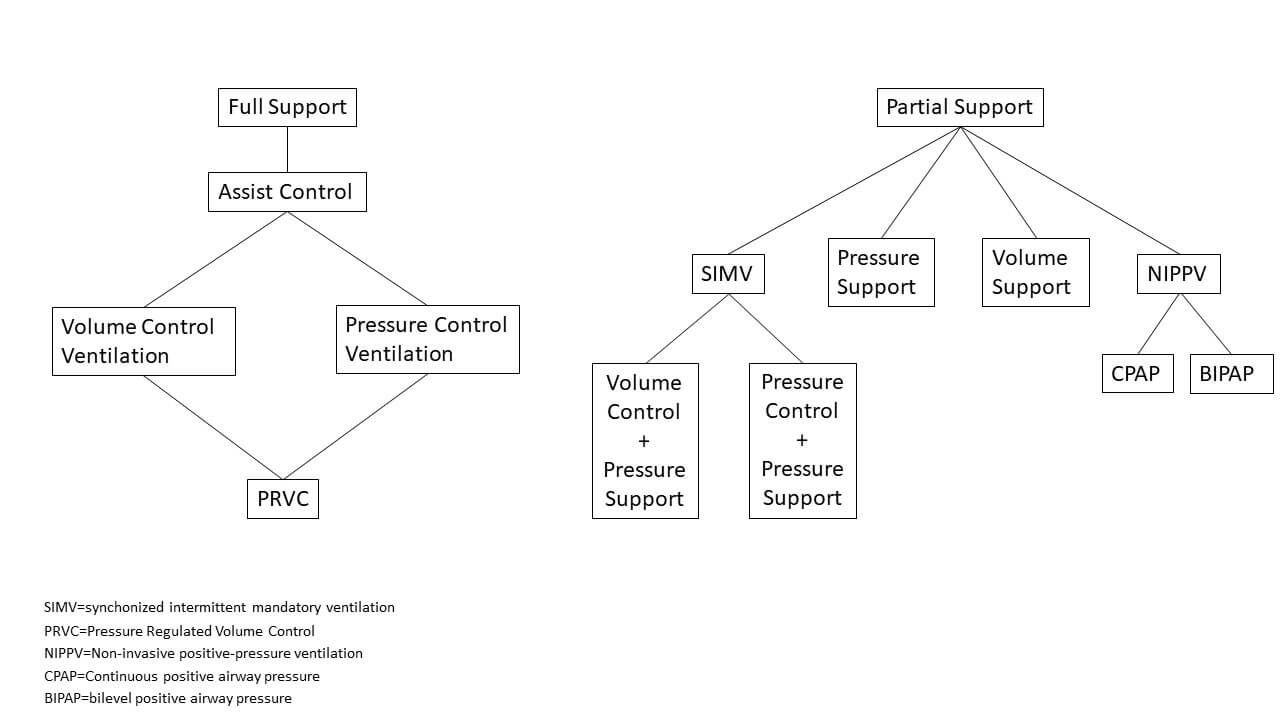
- Materials: They can be divided into Disposable (Single use) and Reusable types. Disposable materials are typically PE/EVA and ESB, while reusable materials are usually Hytrel and Silicone
- Characteristics: According to tubing characteristics, it can be categorized into Corrugated Circuit, Smoothbore Circuit, and Collapsible Circuit

Corrugated Circuits have a flexible, accordion-like structure that allows for easy bending and stretching without kinking

Smoothbore Circuits have an inner surface that is smooth and straight, which minimizes airflow resistance and optimizes gas delivery. This smooth interior allows for easier, more laminar flow of gases, which can enhance ventilation efficiency and reduce work of breathing for patients

Collapsible Circuits have highly flexible and can expand and contract as needed. This property allows for easy length adjustments to accommodate different patient positions and minimize circuit tension
- Configurations: To accommodate different types of ventilators, tubings can be classified as single-limb , double-limb or coaxial

Single limb circuit

Dual-limb circuit
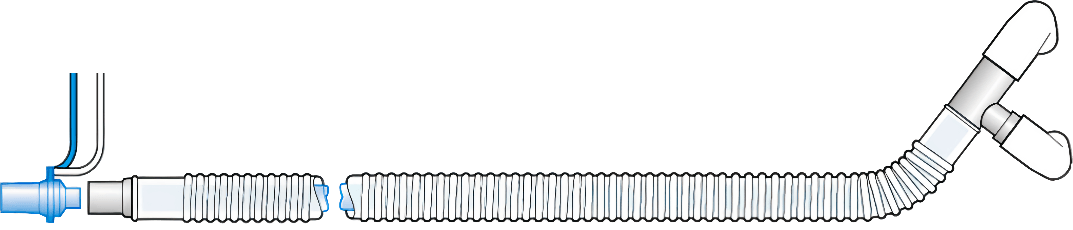
Coaxial circuit
Single Limb Circuit Dual-limb circuit Coaxial circuit Structure Uses a single tube for both inhalation and exhalation Separate tubes for inhalation and exhalation Coaxial design with inner and outer tubes combined Space Requirement Compact, suitable for mobility Takes up more space, less portable Space-saving, compact design Flow Resistance Highest Lowest Moderate Gas Efficiency Inhaled and exhaled gases may mix; higher gas flow needed to avoid rebreathing Good gas separation, reduces risk of inhaled gas contamination High efficiency, minimizes gas mixing Applications Suitable for shorter or lightweight procedures Ideal for longer, precise ventilation needs Suitable for various cases, especially space-limited setups - Heated type: Based on the presence of heating wires, they can be divided into Heated or Non-Heated circuits. Heated circuit can be further classified into Single-Heated and Dual-Heated.
Humidification system
Humidity
Absolute humidity (AH, mgH2O/L)
The actual amount of water vapor in a given volume of air; The weight per volume or as pound per 1,000 cubic feet.
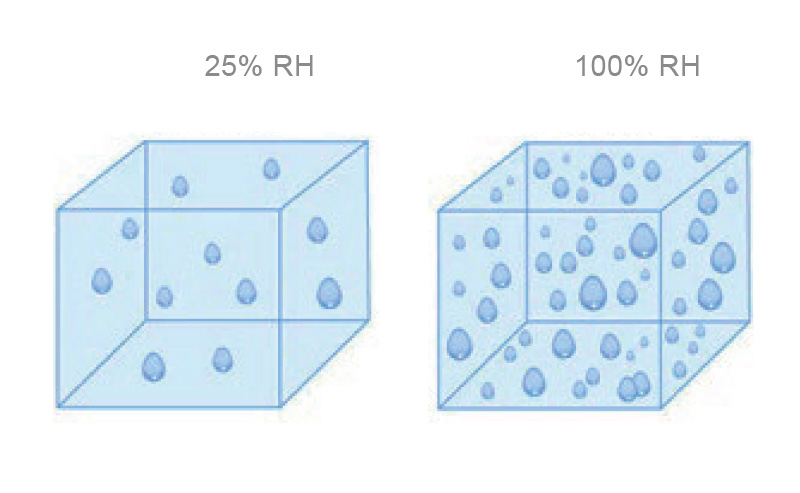
Relative humidity (RH, %)
The amount of water vapor in the air, expressed as a percentage, of the maximum amount of water vapor that the air can hold at a given temperature; the ratio of actual water vapor pressure to the saturation vapor pressure.
Humidity Therapy
- Humidity is essential to the human respiratory system. Dry air (about 10 mgH2O/L) enters the trachea and is conditioned by the tracheal mucosa until it reaches the high humidity of the bronchial bifurcation (44 mgH2O/L). This point is called the Isothermal Saturation Boundary (ISB), where the inhaled air has reached body temperature (37°C) and is 100% saturated with water.
- During mechanical ventilation and anesthesia, the air supplied to the patient is usually colder and drier than the regular air which may result in poor gas exchange and poor inflation of the bronchioles and alveoli.
- Humidity Therapy is a method to artificially condition the gas used in respiration of a patient as a therapeutically modality.
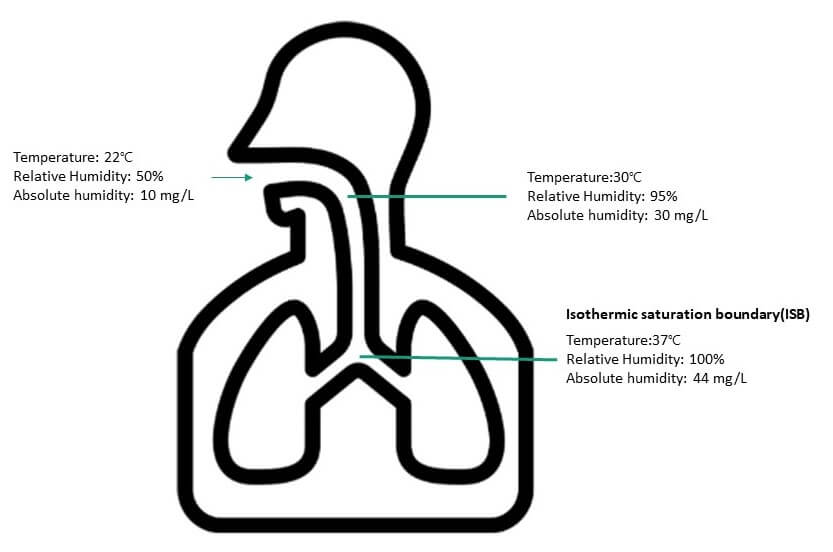
| Temperature | Humidity (AH) | |
| Isothermic saturation boundary (ISB) | 37°C | 44 mg/L |
|---|---|---|
| Medical O2 Gas | 15°C | 0.3 mg/L |
| Room temperature | 22°C | 10 mg/L |
| Oxygen therapy | ambient | 16 mg/L |
| HME | 25 ~ 30°C | 17 ~ 32 mg/L |
| Heated humidifier | 37°C | 44 mg/L |
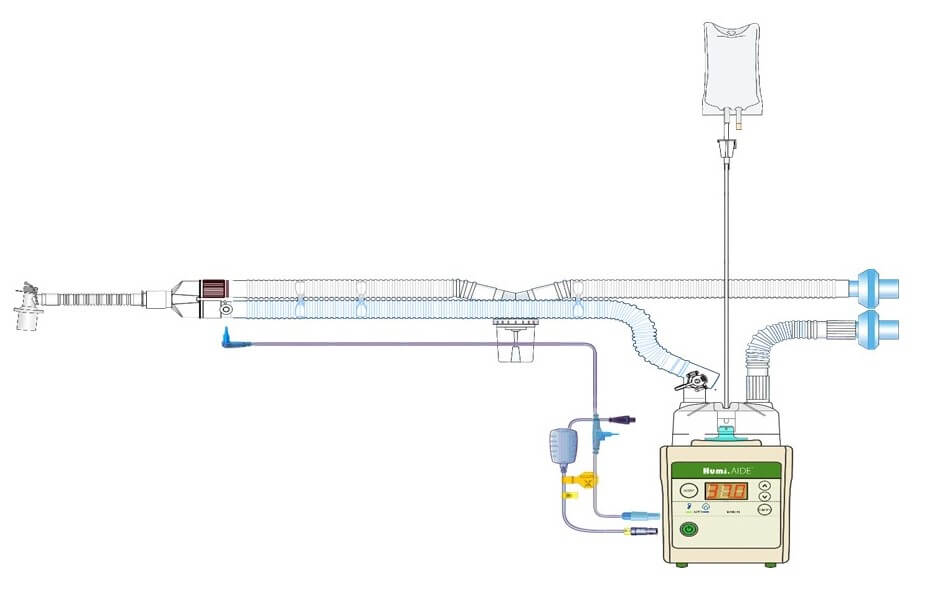
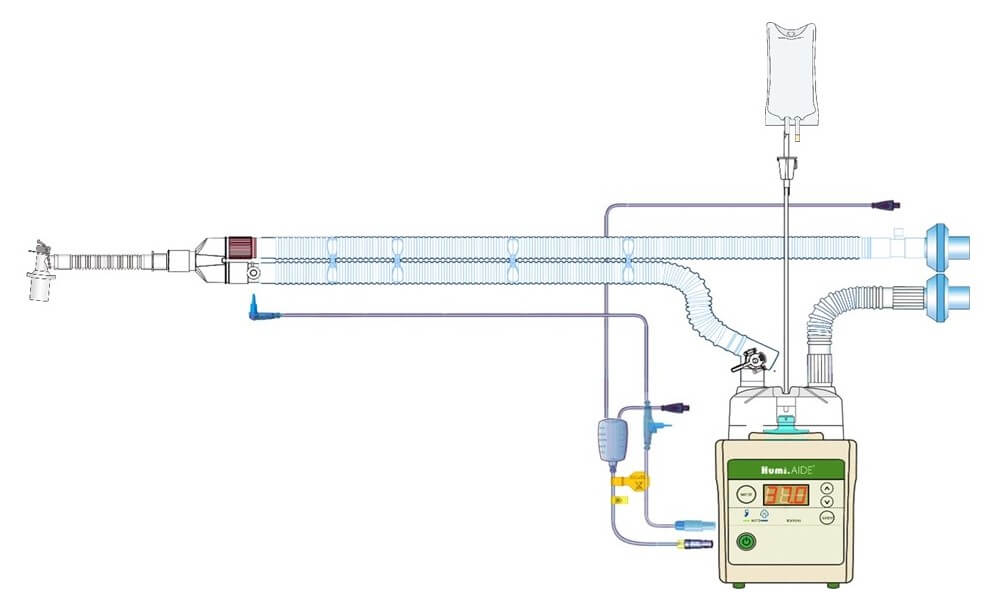
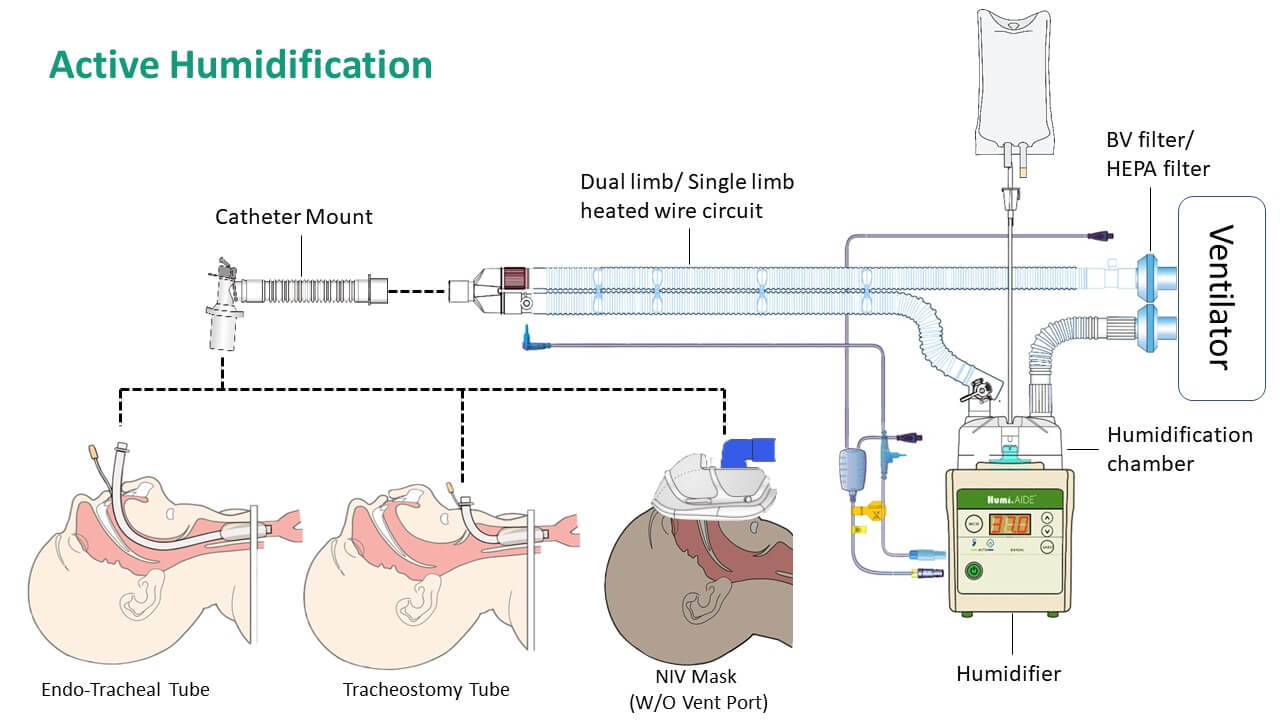
Active Humidification
The supplied gas is optimally conditioned with heat and moisture from an electrically powered humidifier. It mainly consists of a humidifier and a humidifier chamber.
Humidifier
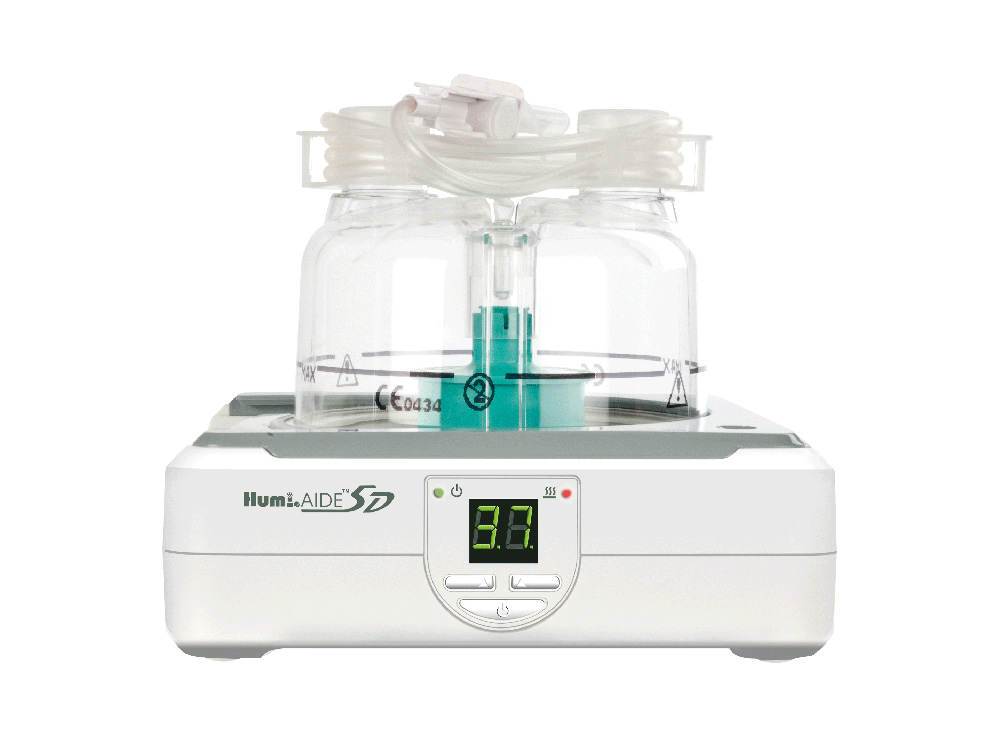

Humi.AIDE™ 5D Humidifier
- Digital type humidifier to set up desired temperature
- With optional temperature probe 5D humidifier is available for temperature monitoring
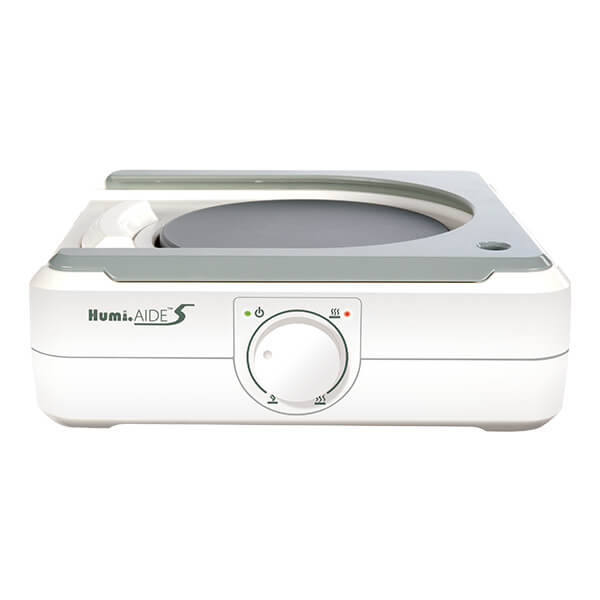

Humi.AIDE™ 5A Humidifier
- Temperature adjustment knob to adjust temperature fast and easily
- Double overheat protection to ensure patient’s safety
Humidifier chamber
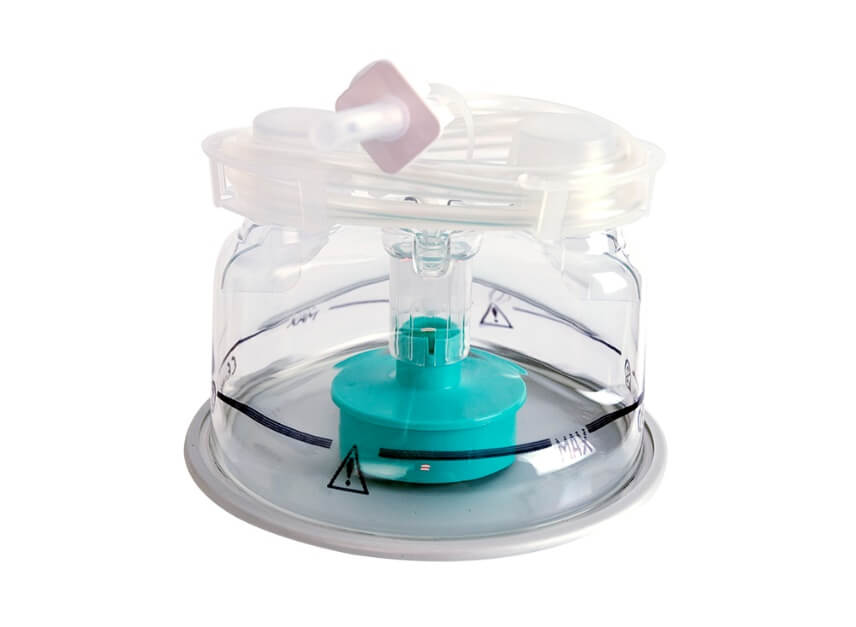
Auto Feeding Humidification Chamber
- Features a sensitive auto-filling mechanism for accurate water level control
- Allows sterile water to automatically fill into the chamber without interruption of flow and ventilation
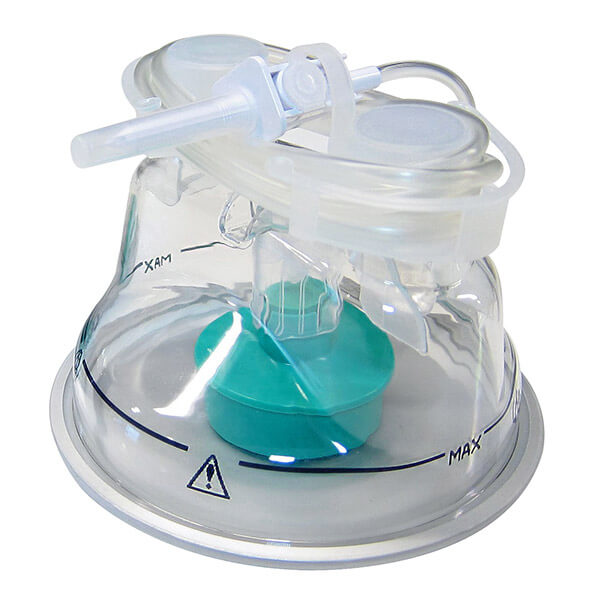
Neonatal Auto Feeding Humidification Chamber
- Low dead space and resistance designed for neonates
- Allows sterile water to automatically fill into the chamber without interruption of flow and ventilation
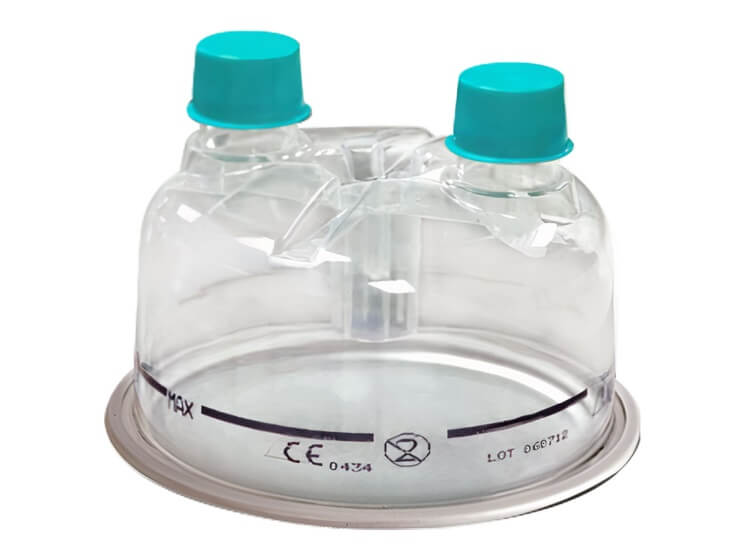

Humi.AIDE™ Disposable Humidification Chamber
- Single patient use
- 360° Viewable Water Line: Easy to monitor the water level from all angles
- Less Heating Time: Lower water level and greater heater contact
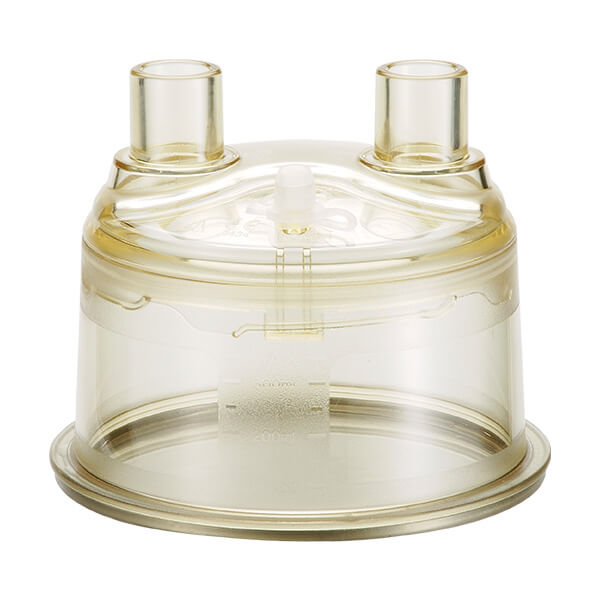

Humi.AIDE™ Durable Humidification Chamber
- Water Fill Port: No need to remove chamber to refill
- Safety Lock: Latch design and silicone ring to provide secure seal and prevent accidental spillage
- 360° Viewable Water Line: Easy to monitor the water level from all angles
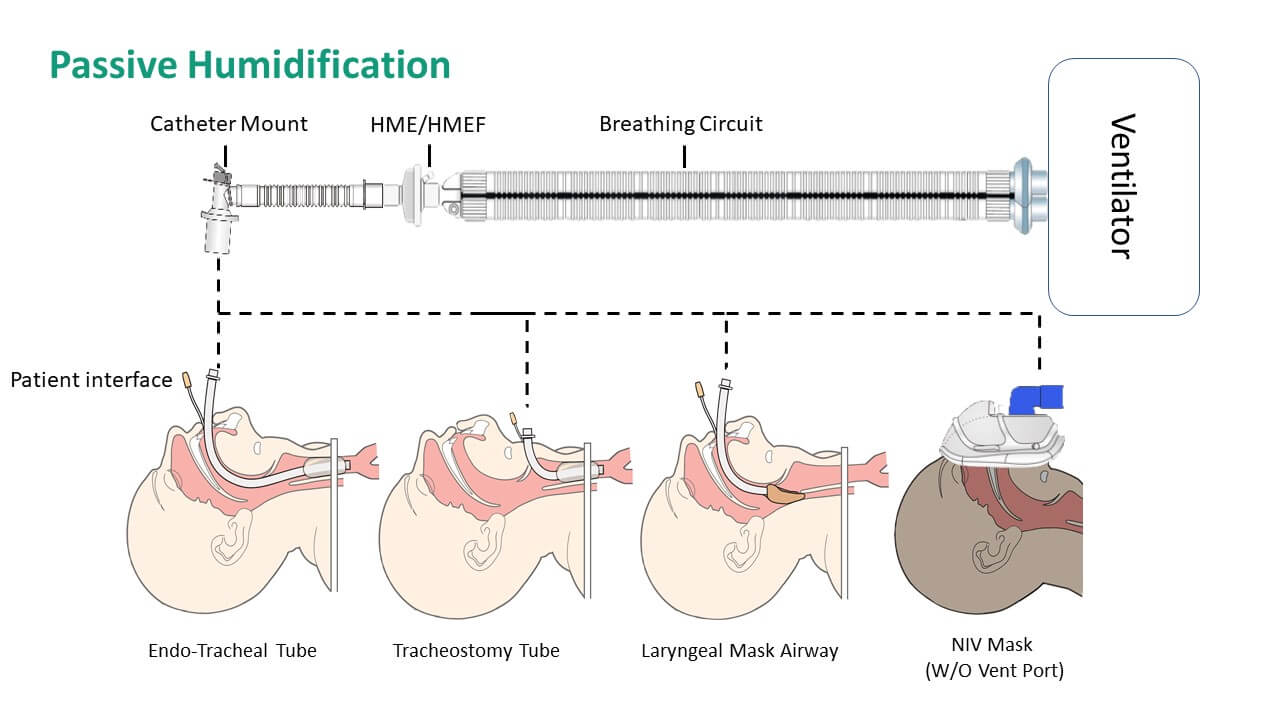
Passive Humidification
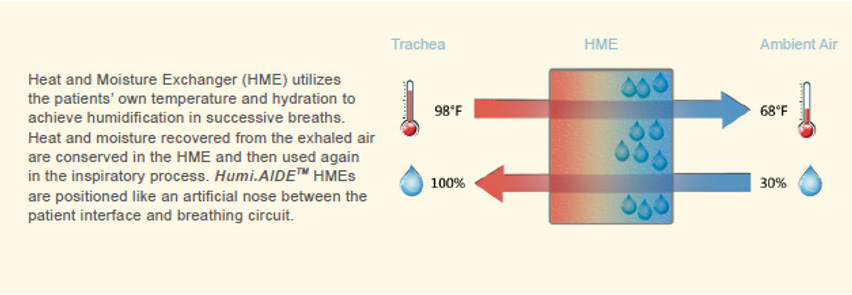
Including Heat and Moisture Exchanger (HME) and Heat and Moisture Exchanger Filter (HMEF). A HME is a medical device used to conserve and return heat and moisture to inhaled gases during mechanical ventilation or in patients with tracheostomies. By mimicking the natural humidifying functions of the upper respiratory tract, HMEs help prevent drying of the airway, which can lead to complications such as mucus plugging, airway obstruction, and infection.
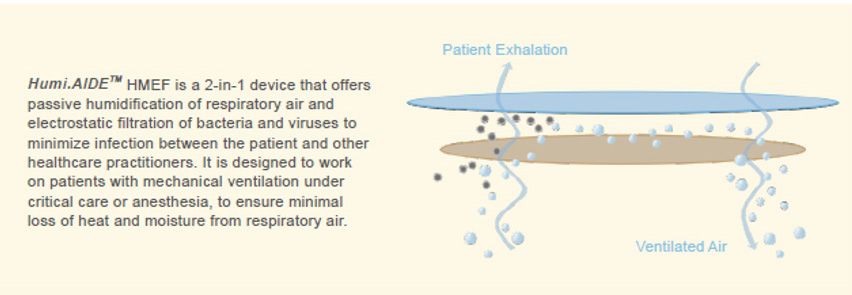
A Heat and Moisture Exchanger Filter (HMEF) is a specific type of HME that combines the functions of heat and moisture exchange with filtration. It provides additional protection against airborne pathogens.
Heat and Moisture Exchanger (HME)
Heat and Moisture Exchanger Filter (HMEF)
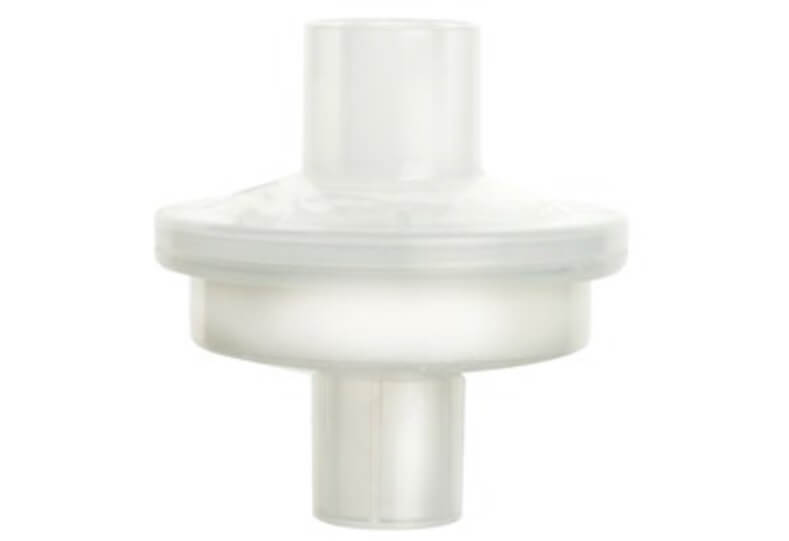

HME
- Paper filter media
- Able to absorb and store the heat and condensation of exhalation to increase the temperature and the level of humidity of inhaled air
- Suitable for surgical ward, anesthesia, respiratory care, and intubated home-cared patients

HME (with Flex Tube)
- Foam filter media
- A Flex Tube allows for easier angle adjustment when connecting to the patient interface
HMEF (Heat and Moister Exchanger Filter)
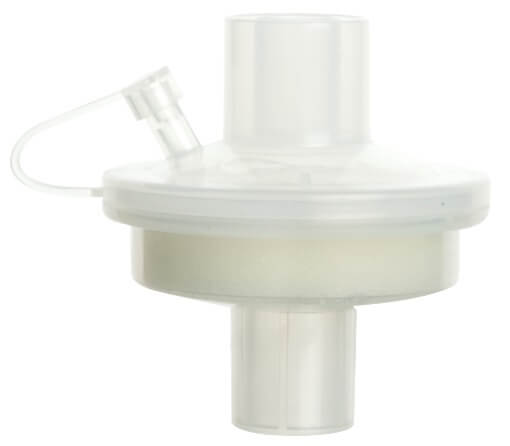

HMEF(Paper)
- Paper filter media
- A 2-in-1 device that offers passive humidification and electrostatic filtration of bacteria and viruses.
- Designed to work on patients with mechanical ventilation under critical care or anesthesia, to ensure minimal loss of heat and moisture from
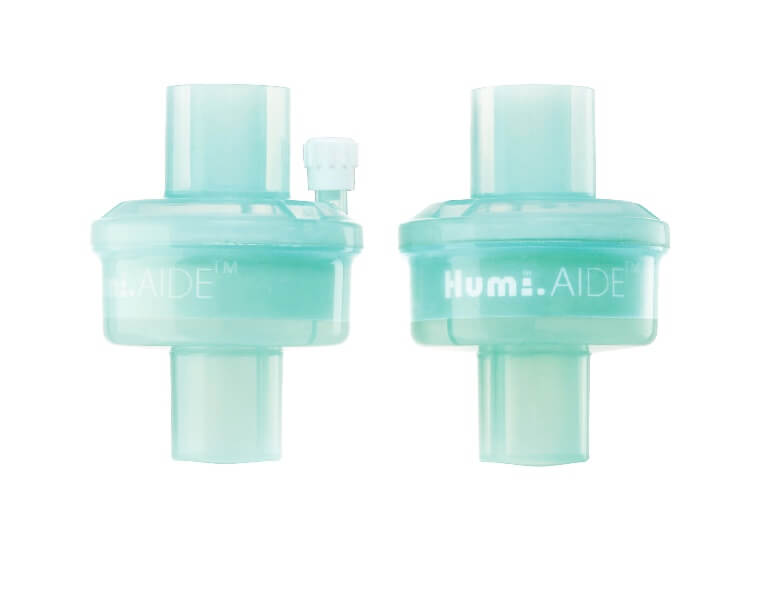

HMEF(Foam)
- Foam filter media
- Filtration: Provide up to 99.99% of efficiency
- Luer Port: For pressure monitoring and gas sampling
Filters
Filters in mechanical ventilation play a significant role in protecting the patients, the device, and the environment from potential contamination. Filters are used to ensure adequate indoor air quality for users in rooms fitted with the ventilation system. The guidelines of British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy recommended the use of expiratory filters for patients suffering from highly communicable infections (e.g., human coronavirus) and who require mechanical ventilation to reduce the contamination of ventilator circuits.
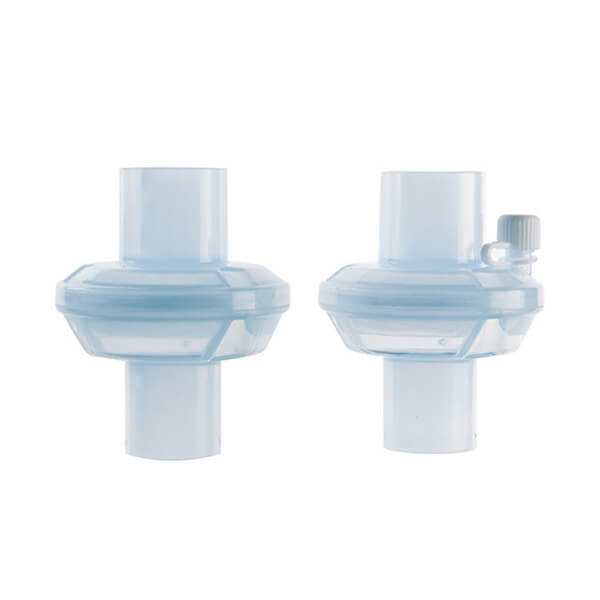

Viral/Bacterial Filter
- High efficiency bacterial filter to minimize cross-contamination between patients, equipment and other healthcare practitioners
- Bacterial & Viral Filtration Efficiency: Up to 99.99%

Bacterial Filter (Foam)
- Equipped with 0.3 micron bacterial filter membrane for up to 99 .99% of efficiency
- Pressure resistance: less than 1 cmH2O/ 50 LPM
- Two different types: with or without Luer

HEPA Radial Pleated Filter (Paper)
- Long term anesthesia/ventilation bacterial filtration up to 99.9999% of efficiency
- Luer Port: For pressure monitoring and gas sampling
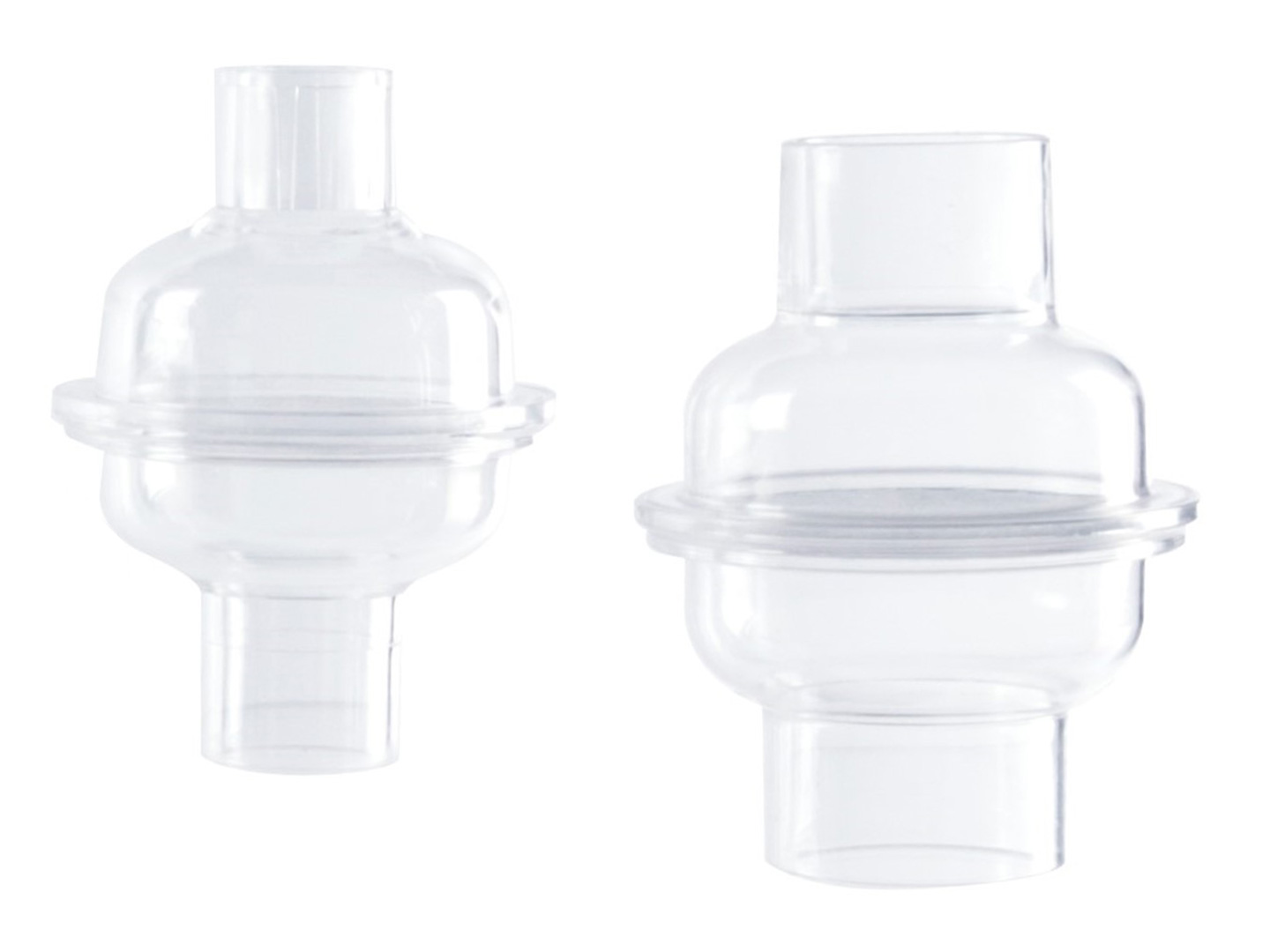

Electrostatic Bacterial Filter
- Electrostatic filter media
- Bacterial& Viral Filtration Efficiency: Up to 99.99%
Accessories & connectors
Manifold
Manifold is used to regulate the flow for the expiratory of the dual or single limb breathing circuits. The control line from the ventilator controls the opening of the valve to enable air to flow out accordingly. J circuit and IPPB circuit are also available GaleMed provide customers more options to choose from.
3 way monifold in single limb circuit
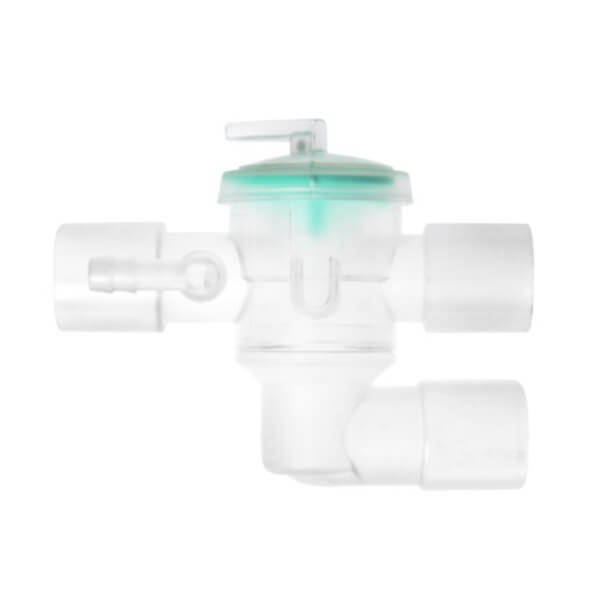
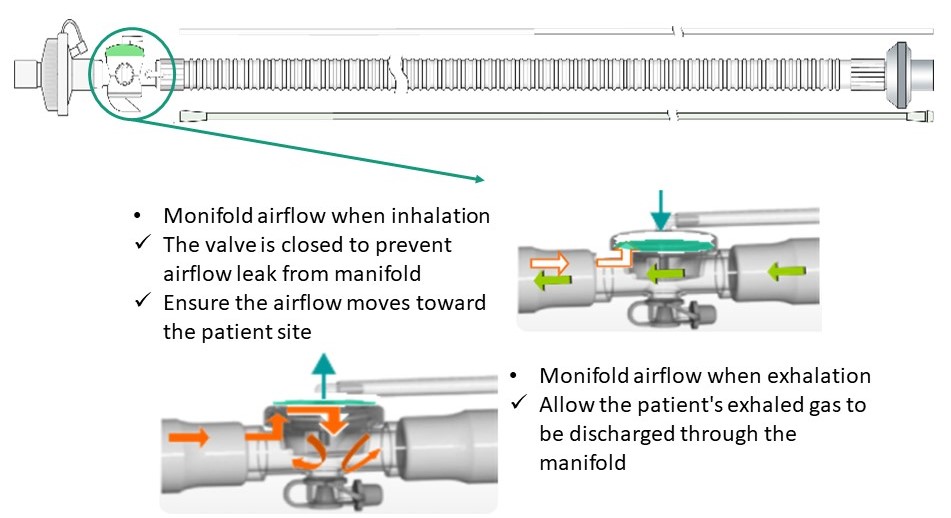

3-Way Manifold
- Designed for single limb circuit
- The control line from the ventilator controls the opening of the valve to enable air to flow in and out accordingly
- Disposable or Durable
2 way monifold in J circuit(dual limb circuit)
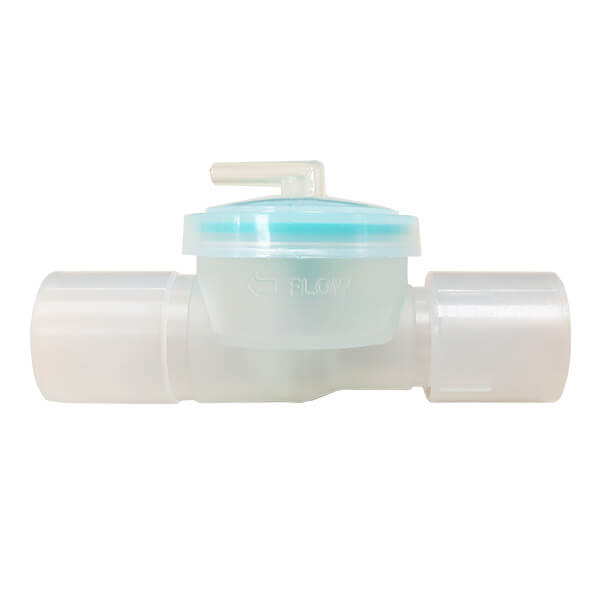
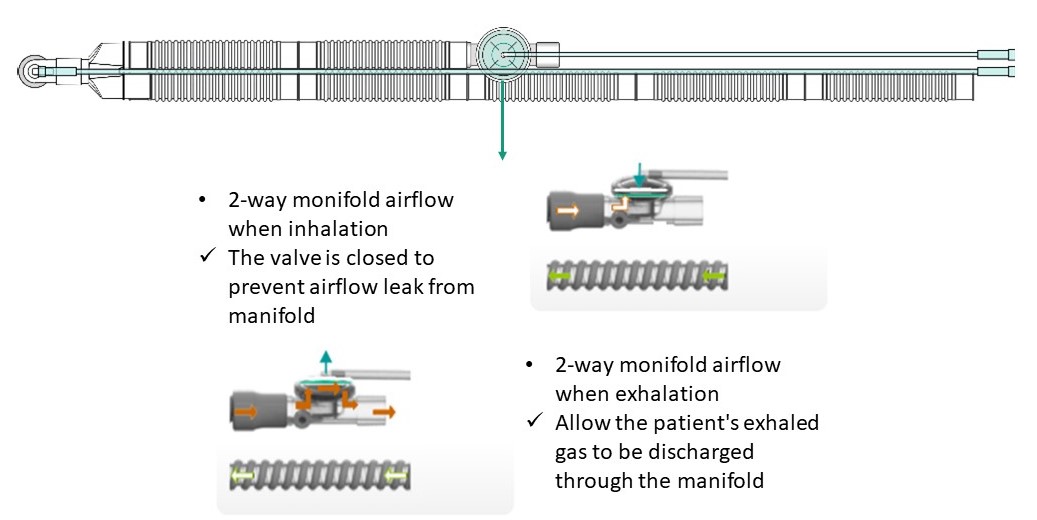

2-Way Manifold
- Designed for J circuit (dual limb circuit)
- The control line from the ventilator controls the opening of the valve to enable air to flow in and out accordingly
- Disposable or Durable
Test Lung
A test lung is a medical simulation device used to mimic the behavior of a human lung for testing and calibrating respiratory equipment, such as ventilators and anesthesia machines. Test lung is an essential tool for testing, calibrating, and ensuring the proper functioning of ventilator, as well as for training healthcare professionals in using these devices safely and effectively.
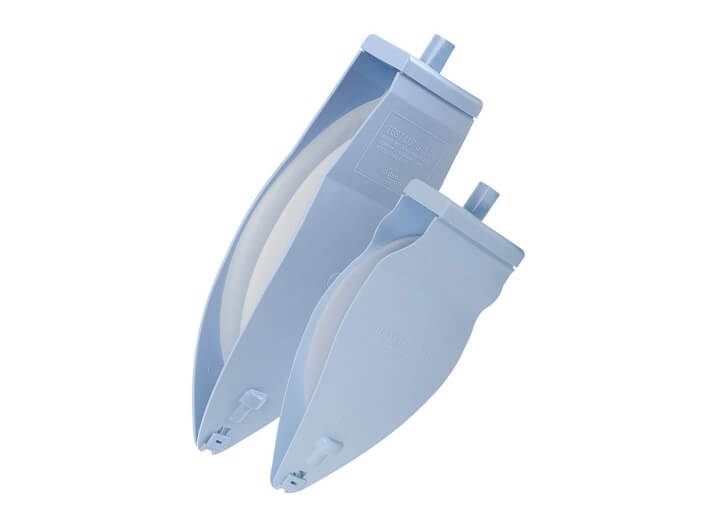

Venti. Plus™ Test Lung
- Simulate level of resistance and lung compliance of adult and pediatric respiratory system to provide consistent accuracy
- Lightweight, easy and convenient for use and storage
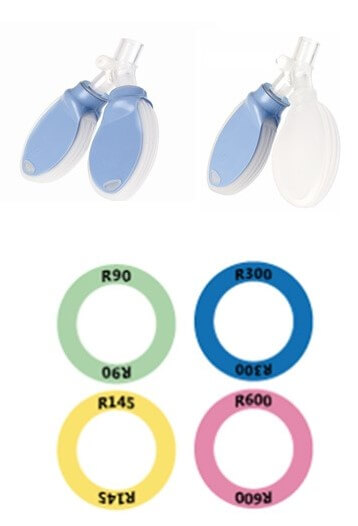
Babi.Plus™ nTest Lung
- With/without bracket generate different compliance
- Pressure monitoring port for measuring proximal airway pressure
- 4 color-coded indicators easily identify the individual lung resistance
Connectors
Connectors in a medical breathing circuit are essential components used to join various parts of the respiratory system, ensuring a secure and seamless flow of gases. GaleMed offers connectors in various shapes, suitable for a wide range of clinical situations, helping healthcare professionals assemble appropriate tubing systems.
Straight connectors join tubing of different diameters. Wye connectors, used in dual-limb circuits, are positioned proximally (nearest to the patient) and merge the inspiratory and expiratory limbs. Tee connectors are needed to assemble other breathing circuit configurations.